Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions
It is not possible to talk about the. Sets with similar terms.

Stat 2040 Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables And Continuous Probabil Oneclass
It measures the number of standard.
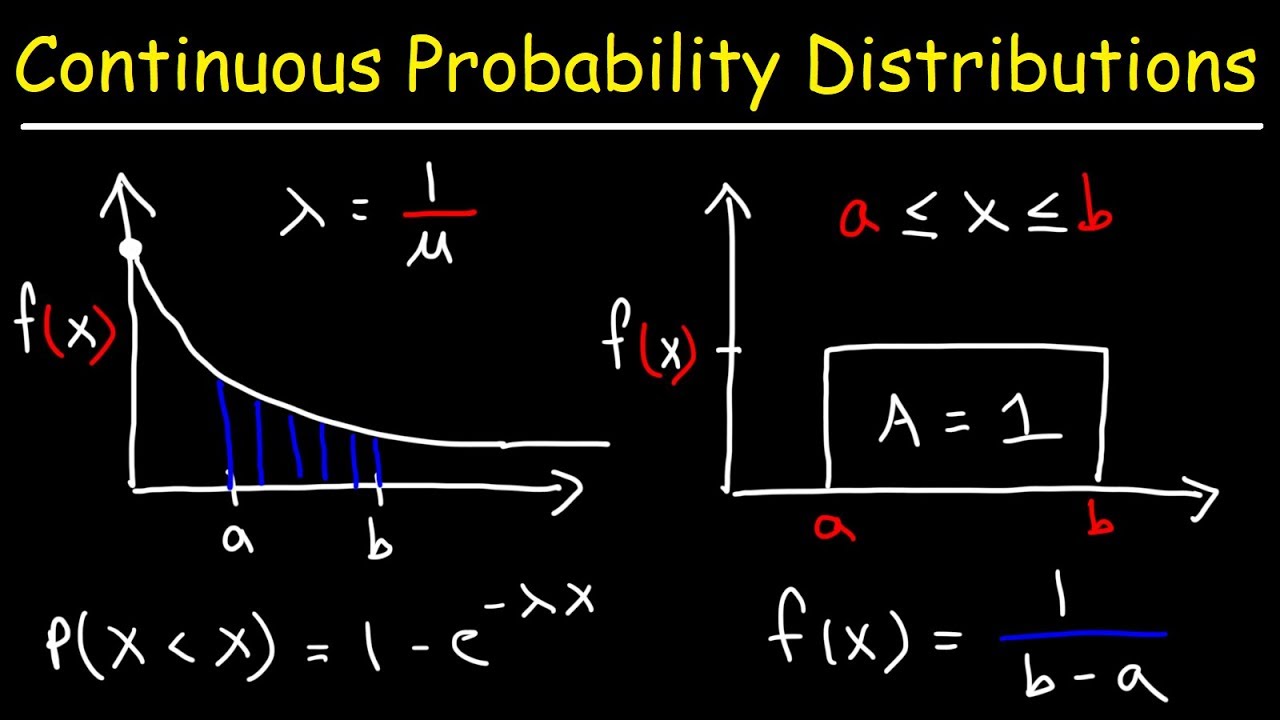
. Continuous Probability Distributions 178 Section 62. If the mean median and mode are all equal for a continuous random variable then the random variable is normally. Graphs of the Normal Distribution Many real life problems produce a histogram that is a symmetric unimodal and.
Or posted to a publicly accessible website in whole or in part. Get 247 study help with. Explain the Standard Normal Density Function in detail.
Introduction to Continuous Probability Distributions 9. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The exponential probability distribution is a.
Up to 15 cash back Chapter 6. Up to 3 cash back AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION Chapter outline 41 Continuous Random Variables 42 Probability Distributions and Probability Density Functions 43. Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Uniform Probability Distribution Normal Probability Distribution.
The standard normal distribution the z distribution Any normal variable with mean μ and standard deviation σ can be converted into the standard normal variable by the following. Start studying Chapter 6. What is p x -1.
A probability distribution associated with the time between arrivals. Continuous Probability Distributions 178 Section 62. The number Xn of such events that occur has a Binnp distribution.
Chapter 6 Continuous Distributions Page 2 are like n independent flips of a coin that lands heads with probability p. A continuous probability distribution that is useful in computing probabilities for the time it takes to complete a task. 14 terms uniform probability distribution whenever the probability is pr uniform probability density function fx 1b-a and then 0 for area of a probability density function area.
Some Continuous Probability Distributions 64 ApplicationsoftheNormalDis-tribution z-score z x m s is often called the z-score. Video answers for all textbook questions of chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Statistics for Business Economics by Numerade. F of z is equal to 1 divided by the square root of 2 pie all times the constant e raised to the negative z squared over 2.
A continuous random variable can assume any value in an interval on the real line or in a collection of intervals. A continuous uniform random variable x has a lower bound of a -3 an upper bound of b 5. A continuous random variable has the uniform distribution of the interval ab if its probability density function f x.
Is constant for all x between a and b and 0 otherwise. Continuous Probability Distributions The probability of the random variable assuming a value within some given interval from x 1 to x 2 is defined to be the area under the graph of the. Graphs of the Normal Distribution Many real life problems produce a histogram that is a symmetric.
A function that represents the distribution of variables as a symmetrical bell-shaped graph.
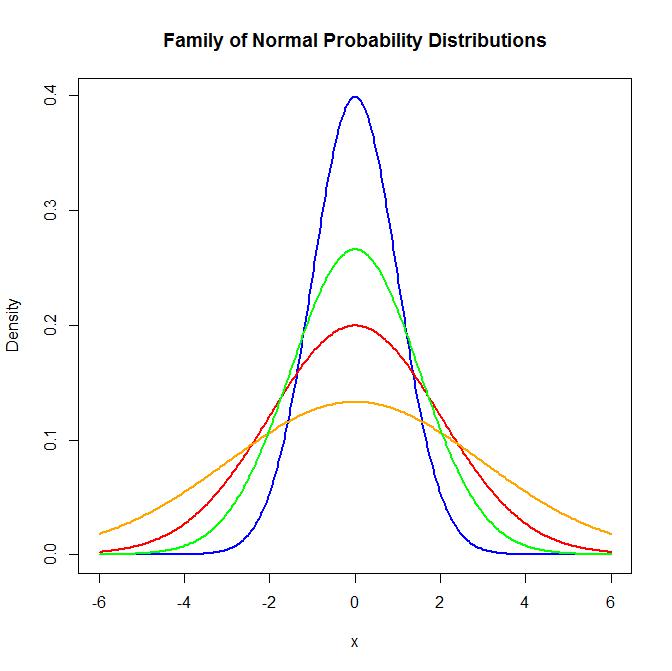
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website

Continuous Probability Distributions Basic Introduction Youtube

Continuous Probability Distribution An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
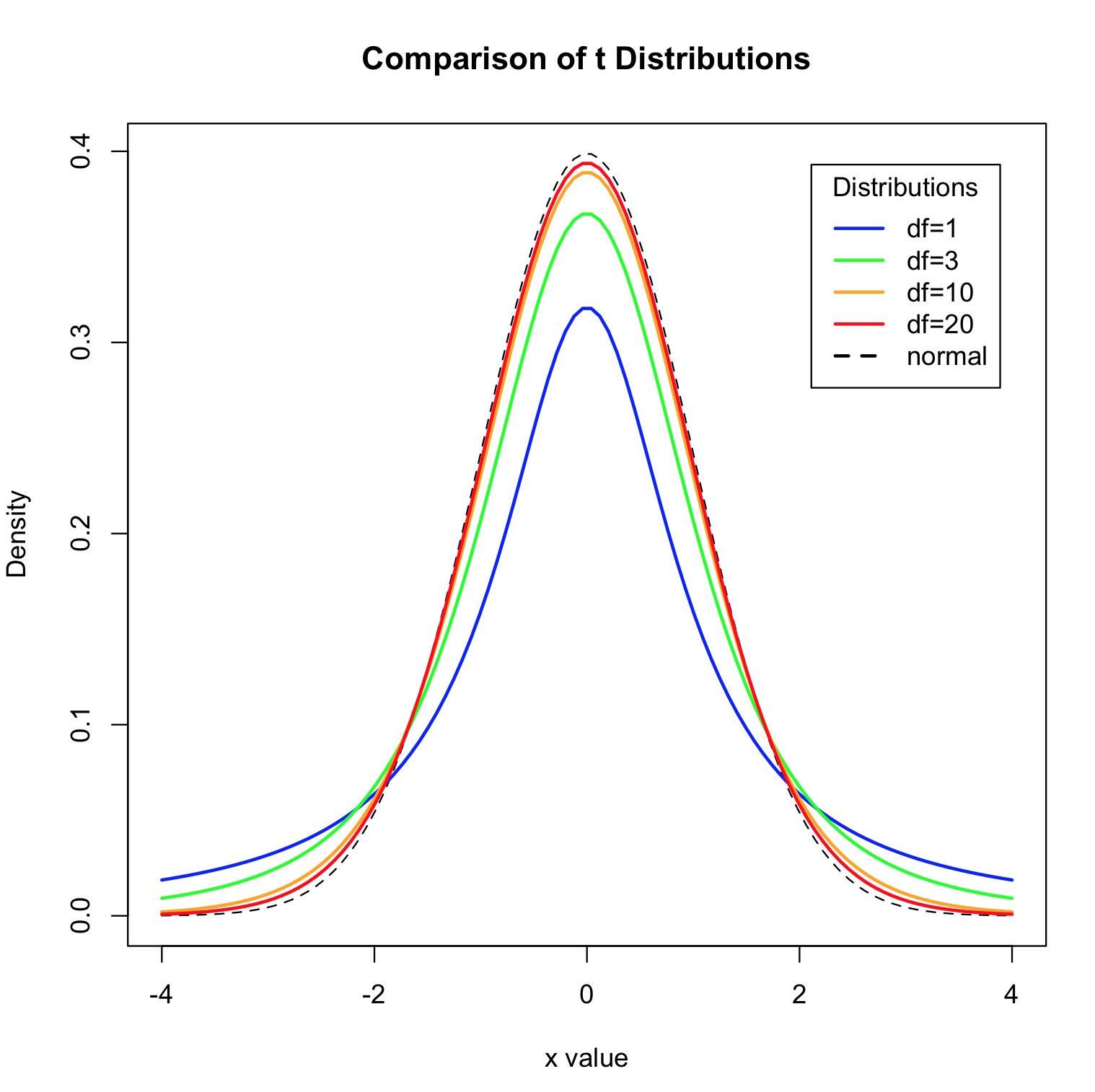
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website
No comments for "Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions"
Post a Comment